Focus is the ability to receive user input through the mouse or the keyboard. The foremost window out of several running applications will have an active (colored-in) title bar; this application is the one which "has focus." Within this application, the foremost window out of any open windows will have an active (colored-in) title bar. This window is the one which "has focus." Within this window, which for the sake of argument is an ATEasy form window, there can be several controls. Out of these controls, only one can "have focus" at any time; only one control at a time can receive text input or mouse clicks.
Most form controls support the GotFocus() and LostFocus() events. These occur when an object receives or loses focus. In order to give an object focus, you can select it at run time with the mouse, use a shortcut key (if available) to select it at runtime, or use the SetFocus() event in your procedure. LostFocus() is especially useful for verifying or validating input field contents.
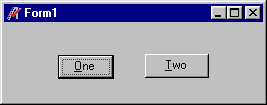
You can see when some objects have the focus. For example, when command buttons have the focus, they appear with a highlighted border around the caption. Here, the button marked "One" has focus.

An object can receive focus only if its Enabled and Visible properties are set to True. The Enabled property allows the object to respond to user-generated events such as keyboard and mouse events. The Visible property determines whether an object is visible on the screen.
Certain controls, such as ALabel, AImage, and ATimer, cannot receive focus.