An I/O Table contains a list of operations communicating with a device through an ATEasy interface, such as GPIB, RS-232, File, and more. The I/O Table can only be defined under a driver's I/O Table submodule. Once defined, an I/O Table is interface-independent and can work with all supported interfaces of a device (for example, a DMM with RS-232 and GPIB interfaces). I/O Tables contain the following operations: Output, Send, Receive, Input, Delay, or Trigger. These operations are explained in Types of Operations.
In the simplest I/O Table, the following occurs:
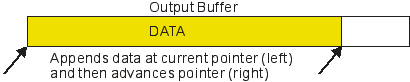
1. As
shown in the following diagram, an Output
operation appends data at the current pointer and then advances the pointer
to where the newly-appended data in the buffer ends.

2. A Send operation transmits the data from the Output buffer to a device, flushes the buffer, and moves the buffer pointer back to the beginning of the buffer.
3. As shown in the diagram, a Receive operation flushes the Input buffer, then reads the data and puts it into the Input buffer, and then sets the pointer to the beginning of the Input buffer.
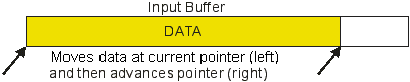
4. An
Input operation moves data from
the Input buffer into a variable and moves the buffer pointer forward
for the next Input operation.
I/O Tables can send or receive data to a device, regardless of the interface. Through I/O Tables, data is sent to, and received from, instruments while ATEasy handles all of the low-level requirements of the communications protocol.