Defining DLL Procedure Parameters
Parameters are variables that hold arguments passed to a procedure when
the procedure is called by another procedure.
To define a procedure parameter:
Select the procedure in the
DLL Procedures submodule for
which you want to define a parameter.
Right-click and select Insert Object Below ( ). ATEasy inserts a new parameter below the
selected procedure.
). ATEasy inserts a new parameter below the
selected procedure.
Right-click and select Properties. ATEasy
displays the new procedure parameter's Properties window:
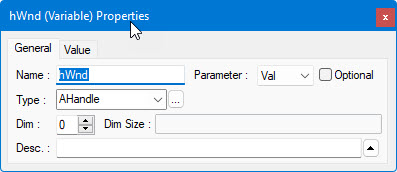
Click the Parameter
drop-down list and select one of the following:
Val if the
actual argument is assigned to the parameter. Arguments can be literals
(for example, 7), expressions (for example, [A+B]), or variables (for
example, dA). Changing the value of the argument in the DLL procedure
does not change the argument. (For a list of compatible data types for
Val parameters, see Compatible
Argument Types.) Select the Optional checkbox to make this parameter
optional. Otherwise, leave the checkbox blank if the parameter is required.
Var if the
parameter refers to the argument and can change the argument value. Arguments
passed by Var must exactly match the data type used in the procedure for
that variable. If you check Optional checkbox with Var parameter, its
initial value is set to Null
- for the case the caller does not supply its Var parameter.
Specify the parameter's name,
type, dimension, dimension size, and description. For more information
on these properties, see Variables
Properties Window. Note that DLL procedure parameters can be defined
as type Any, which accepts
any data type.
When you specify the procedure parameter's data
type, make sure that the ATEasy
data type that you select is the equivalent of the data type of the parameter
in the DLL. For a list of DLL parameter types and their ATEasy equivalents, see DLL
Procedure Parameter Types.
![]() ). ATEasy inserts a new parameter below the
selected procedure.
). ATEasy inserts a new parameter below the
selected procedure.