When you declare a DLL procedure in an ATEasy application using an alias, you can refer to the ordinal number that identifies the procedure in the DLL rather than to its name.
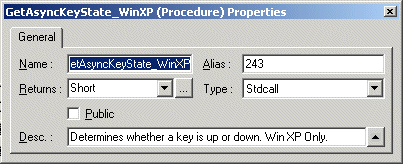
For example, GetAsyncKeyState is a function defined in Windows User32.DLL that determines whether a key is up or down at the time the function is called. The function's ordinal number is different on different versions of Windows. For example, in Windows XP the ordinal is 243 while in Windows 10 the ordinal is 1798. You can use a software called Dependency Walker (www.dependencywalker.com) to check ordinal number of DLL functions. When declaring GetAsyncKeyState with an alias, you can refer to its ordinal number as shown below:

Note that the ordinal number of the procedure in the DLL, "243" is in the Alias field, while the function name that you are declaring within ATEasy, "GetAsyncKeyState_WinXP" is in the Name field.
The example below calls the "GetAsyncKeyState" based on the Windows version:
dwVersion=Kernel32.GetVersion()
! windows 2000 - safe to call
select dwVersion and 0xFFFF
case 0x106 ! Windows 7
if User32.GetAsyncKeyState_Win2K(VK_CONTROL)<0 ! key is down
TestStatus=FAIL
endif
case 0x105 ! Windows XP
if User32.GetAsyncKeyState_WinXP(VK_CONTROL)<0 ! key is down
TestStatus=FAIL
endif
endselect