Automated Test System
An Automated Test System, also
referred to as Automatic Test Equipment (ATE), is a collection of instruments
under computer control performing automated test functions.
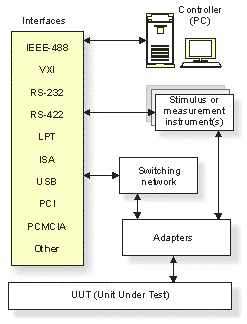
The diagram below shows a typical configuration of an ATE system. A
computer provides control over test and measurement instruments by using
hardware interfaces. The instruments, such as measurement, stimulus, switching,
power and digital are connected to a Unit Under Test (UUT) through an
adapter.
|
The
most common computer used in ATE applications is the PC. Due to
its relatively low cost, computing power, and the availability
of hardware interfaces and computer programs, the PC has become
the de-facto standard of the test industry.
The PC supports numerous methods called
interfaces for controlling test instruments. These interfaces
include IEEE-488 (GPIB), VXI, ISA bus, PCI Bus, and RS-232. Software
programs such as ATEasy allow
the computer to control test instruments using any of these interfaces. |
Test instruments include:
● Measurement - instruments measuring
electrical characteristics
● Stimulus - instruments generating
electronic signals
● Digital - instruments that read
and write digital patterns
● Power - instruments using power
sources
● Switching - instruments routing
electrical signals to different points
The adapter, also referred
to as Interface Test Adapter (ITA), routes the signals from the test system
to the Unit Under Test (UUT), which is the target of the ATE.
Under software control, the computer performs test sequences and procedures
used to determine if the UUT is performing according to its specifications.
Controlling the test instruments, routing signals to various test points
in the UUT, and measuring UUT responses achieve this performance determination.
ATEasy provides all the tools required
during the development, debugging and integration of test sequences and
procedures.