Matching Requirements of External Programs
External programs often use structures as arguments. Without the ability to define and create structures in ATEasy, you could not (directly) communicate with these programs.
The following example shows how to match a C-Style structure to an ATEasy structure. Two structures are used: POINT defines an (x,y) coordinate and MSG contains information from a Windows application queue.
|
C-Style Structures
The following code shows the C-Style structures.
|
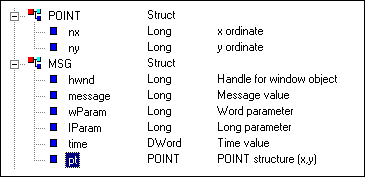
ATEasy-Style Structures
The following ATEasy structures match those defined by the C code.
|
|
struct POINT { /* pt */
int X;
int Y;
} POINT;
struct MSG
{ /* msg */
HWND hwnd;
UINT message;
WPARAM wParam;
LPARAM lParam;
DWORD time;
POINT pt;
} MSG;
|
|
For more information on structures, see About Structures.
