Using Commands
Before you can insert a user-defined command as code, make sure you are in one of the code views, for examples:
You can insert commands during coding in one of three ways:
-
Code Completion - this is the best way to insert commands as illustrated below.
-
Select the command from a menu. This method minimizes syntax errors caused by mistyping.
-
Type the command manually in code view. You can type a command into a test in the same way that you can type code into a test. However, this method can produce syntax errors.
Insert a command using Code Completion:
-
Start typing a module name: for example, Profile, TestExec, or its generic module names - Driver, Program, and System.
-
As soon as you enter a space after the module name, all the commands of the module will presented in a listbox for you to select one desired. Select one of first level commands. Then the command name will be inserted into the code view. If you have further commands after that, the sequence of steps are same; namely, as soon as you give a space, ATEasy suggests with next level commands for you to select and so on... See Completing Code Automatically as well as an example below:
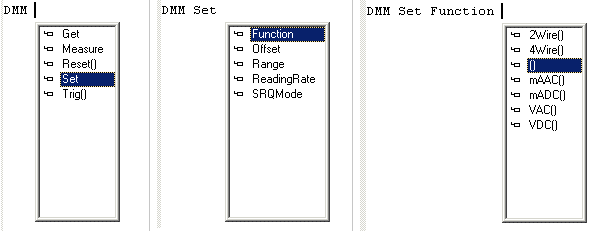
-
If the Command procedure has a parameter, ATEasy will also suggest its selection as follows:

To select a command from a menu:
-
From the Insert menu and select System Command, Driver Command, or Program Command, depending on the type of command you want to use.
-
A popup menu appears listing the available commands. Select the command and release the mouse. The command appears in the coding area of the procedure or test. You can edit the command as needed. The following examples shows that the Driver command DMM Set Function (iFunc) is selected.
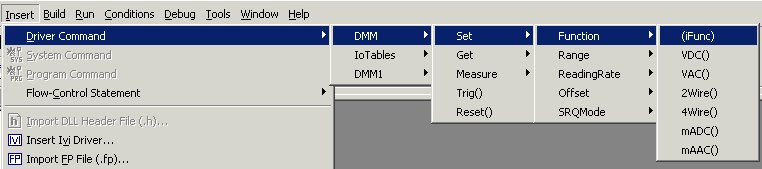
The menu only enables commands available to the module you are currently using. Commands that are not accessible to your current module are disabled. For more information on command access, see Where to Create and Use Commands.
For information on testing and running program code, see Programs, Tasks, and Tests.
For a list of all the steps needed to define a command, see Creating Commands.


