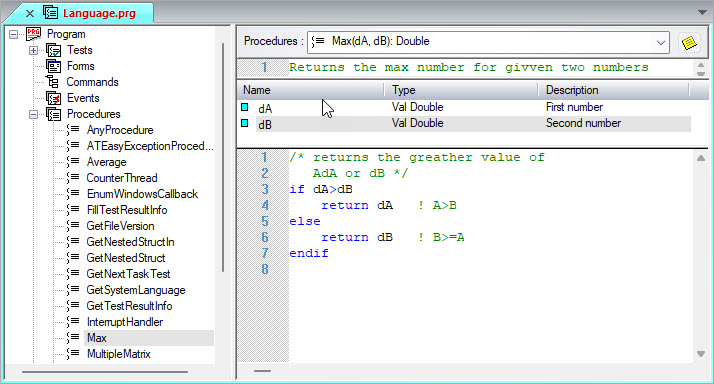
You can enter programming code in the Code area of procedures and tests.
The following example shows the coding area for a procedure.

You click in the coding area to make it active and enter code. ATEasy automatically colors syntax elements so you can easily distinguish them. ATEasy also provides several features to simplify code entry as explained in Bookmarks, Completing Code Automatically, and Controlling Text Entry Options. You control many of these features in the Text Entry tab of the Options dialog as explained in Text Editor Options.
During coding, you can also use the Edit menu: List Members, Show Parameter Suggestion, Show Parameter Information, Show Type Information.
You can also use the Context menu when entering code, which is explained in Context (Right-Click) Menu.
During entering code, through the Context menu or Edit menu, Go To Definition Of menu lets you see the definition of a symbol.
When you are coding for a test, a procedure or an event, you can navigate between tests, procedures, or events by pressing Ctrl+F6, Next Code and Ctrl+Shift+F6, Previous Code accelerators.
For information on procedures, see Creating Procedures. For information on tasks, see Overview of Programs, Tasks, and Tests.
You can break a long statement into multiple lines in the Code window using the line-continuation character (a backslash, '\'). Using this character can make your code easier to read, both online and when printed. The following code is broken into three lines with line-continuation characters (\):
WritePrivateProfileString("+"+App.Name,\
"ProfileSelected",str(m_bProfileSelected),\
m_sOptionsFile)
You can insert comments inside the code. The ! character is used to indicate that the text following the ! character is a comment for the rest of the line:
iCounter=0 ! initialize counter
You can insert comments across multiple lines. The comment start with the /* combination and ends in the same line or one of the next lines with */:
iCounter=0 ! initialize counter
/* This is a multiple
line comment */
...